FMD : 1
It is an acute contagious viral disease.
Symptoms
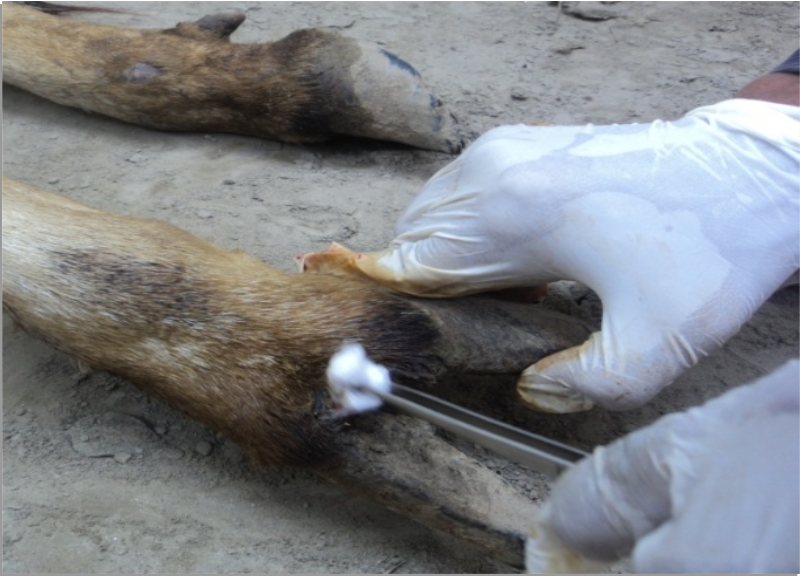
The blisters will appear on the mouth, tongue and foot
Stop feeding due to pain in the mouth and leg
Treatment
Wash the infected part of mouth and leg with
disinfectant
For good result use of antibiotic or sulfonamides
injection
The infected animal should be kept in a dry and clean place and provided with soft or
liquid food
The dead animal must be buried under soil.
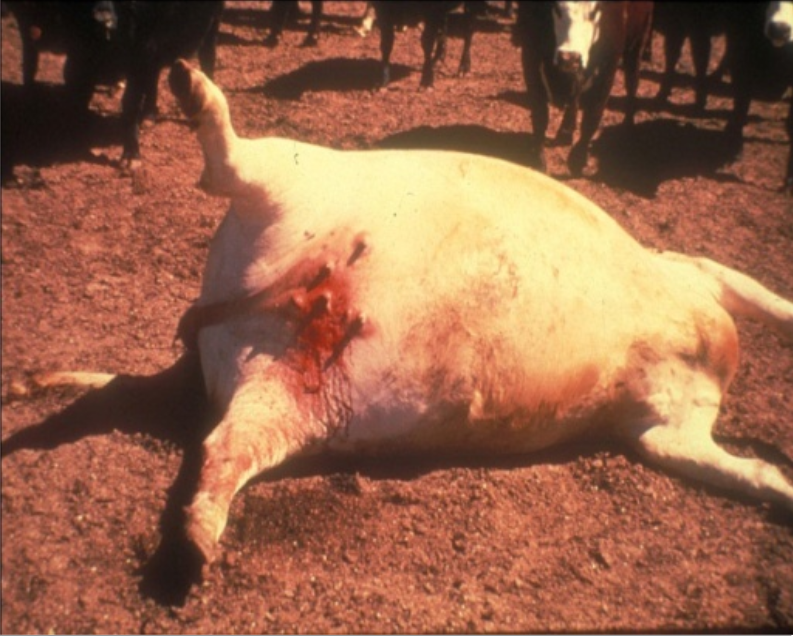
Anthrax :
2
It is an acute contagious bacterial disease.
Symptoms
Lack of appetite, rapid breathing, bloat and abortion
Bleeding through from nose, mouth, vagina and rectum
Hemorrhage in different internal organs
Treatment
Use of antibiotic and antiserum (100-250 ml antiserum per
buffalo,
IV)
Antiserum 8-20 ml; each animal should be injected
intravenously
At the same time, antiserum and antibiotic injection are more
effective
Use of penicillin twice daily (10,000 unit per kg body weight)
The dead animal and their discharge must be buried under soil with lime and the farms
must be
disinfectant with 10% formalin.
Black
Quarter (BQ) :
3
It is an acute contagious bacterial disease. Mainly two years of age groups are more
susceptible.
Symptoms
Two type of symptoms are there (acute and per acute).
The affected areas are swollen, rodent and lameness
Pressing on the affected area will result in sound
Treatment
Use of penicillin twice daily (10,000 unit per kg body
weight)
At first, use of crystal penicillin (IV)
Then procaine penicillin half dose into the muscle twice daily
for 5-7
days
The dead animal and their discharge must be buried under soil with
lime and the farms must be disinfectant with 10% formalin.
Hemorrhagic Septicemia (HS) : 4
It is an acute contagious bacterial disease.
Symptoms
Sudden increase of body temperature (105°-107° F)
Swelling under the throat and increase up to breast
Respiratory disorder and secretion from the nose and
mouth
Sometime swollen the tongue
In sever case, death occurs within 24 hours
Treatment
Use of penicillin, streptomycin twice daily (10,000 unit per kg
body
weight, IM)
Use of antihistamine (IM) for 2-3 days
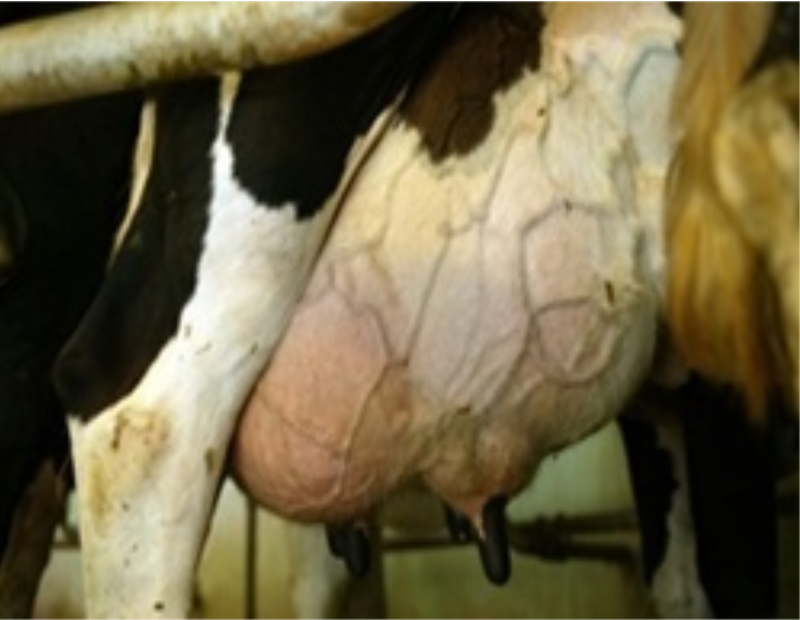
Mastitis
: 5
Inflammation of the glandular tissue of udder is called mastitis or udder swelling.
Treatment
Use of antibiotic and pain killer
Cold water spray for 10-15 minutes by pipe
Before milking, wash the hand and udder with clean water, then
swab with
cloth
Milk
fever : 6
The disease is more prevalent in cows that give more milk.
The disease occurs when the amount of calcium in the cow's blood is less than 5 ml.
Symptoms
Lack of appetite, paralysis and drowsiness
The pupil get bigger and tongue comes out
Laying down on breast region
Unconsciousness, bloat and death
Ketosis :
7
It is a metabolic disease. The disease occurs in more milk producing cows.
Deficiency of glucose in the blood is the cause of the disease.
Symptoms
The effects of the disease are most likely to be seen within
5-6 days of
parturition
Usually the first month of childbirth is in highest risk,
relatively less in the second month,
and rarely occurs during pregnancy
Lactation
tetany : 8
Magnesium deficiency is a deadly disease.
The prevalence of the disease is highest within two months of childbirth.
This disease is caused by feeding animals only grass.
Symptoms
Sometime get excited and jamping
Increase temperature and respiration rate
Diarrhea and frequent micturition
Death within one hour of treatment
Bloat/Tympany : 10
Excessive amount of gas in the abdomen.
Symptoms
At first, left flank become swells and then whole abdomen
swells
Kicking in the stomach, raising frequently, occasionally laying
to the
ground
There is a special sound when taping with a finger on
belly
Without treatment buffalo may be die.
Bloody
urine or
Babesiosis : 11
Tick and mite are the major cause of this disease.
Earlier, there could be a decline in production as well as up to the death of the
animal.
Animals are generally not infected with this disease until the age of 9 months.
Symptoms
Lack of appetite and high temperature (103°-107° F)
Increase breath rate and heart bit
Anemia and blood in urine
Infected animals die within 4-8 days if not treated
properly
Treatment
Use of diminagin diaceturate ( Barenil, babcop vet, (0.8 ml per 100kg body weight, IM)
Use of Imidocarb diproponet (1.2 ml per 100kg body weight, SC)
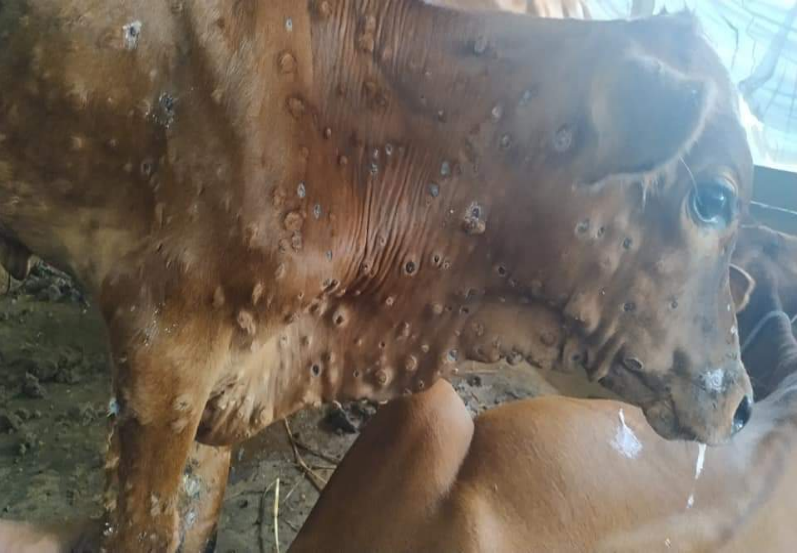
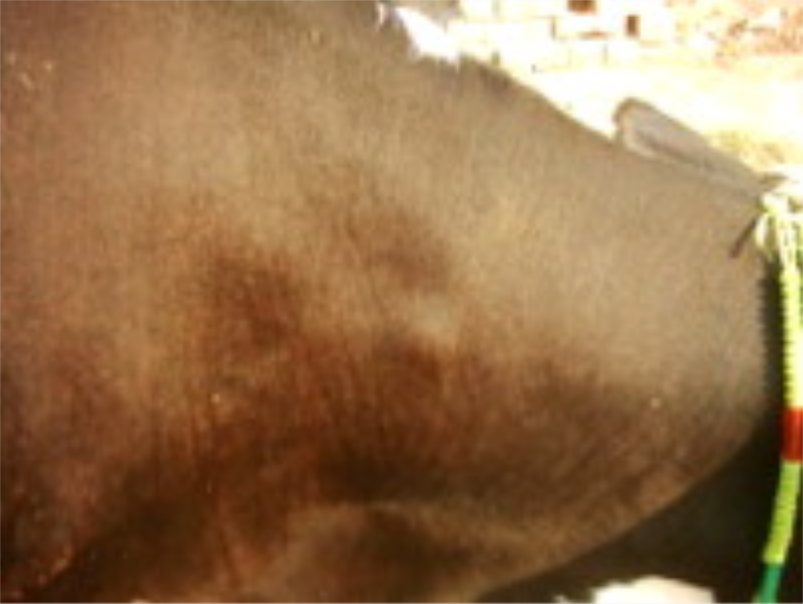
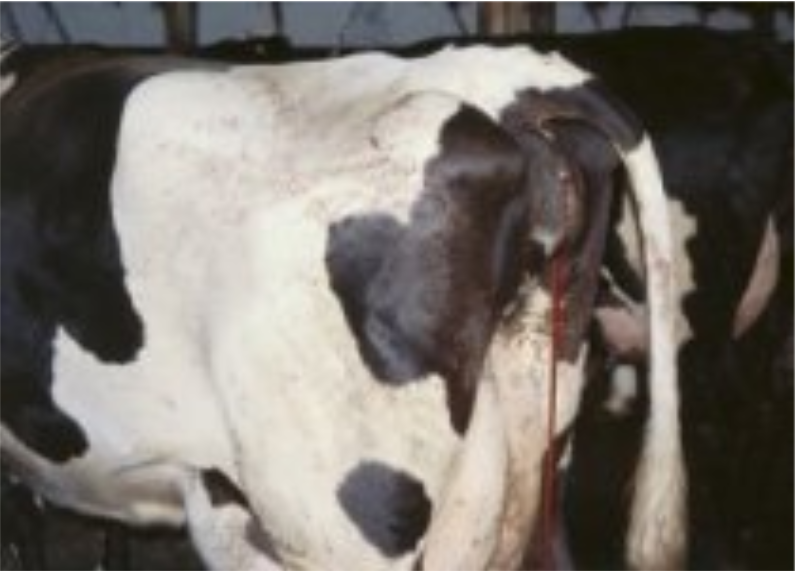
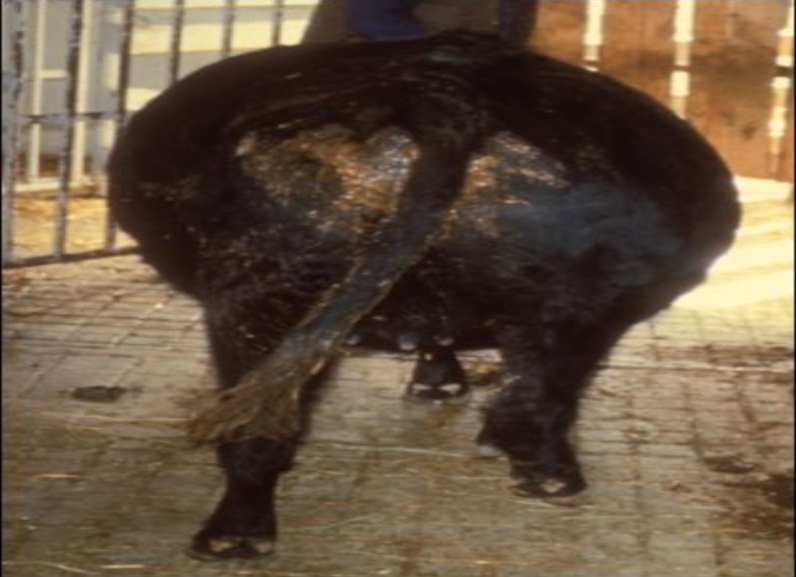
Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD) : 12
When Capri-pox virus infected the cow then it is called Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD).
It is tick borne disease (Mosquito, mite, tick, fly) and transmitted by salivation,
milk, cough and
semen.
Symptoms
High temperature (104°-105°F) and oro-nasal secretion
Blisters or abscesses can be seen under the skin of those
animals
Tearing, corneal opacity and lack of appetite
Treatment
When the blisters of an infected animal are cleared,
it should be cleansed with either the proviso solution or the iodine mixture
Feeding plenty of saline with molasses
Provide mineral supplement (Ferrous sulfate, copper sulfate, cobalt, zinc supplement)
and use of
vitamin-B complex injection
Use of antihistamine, pain killer, antipathetic and Invective for treatment purpose